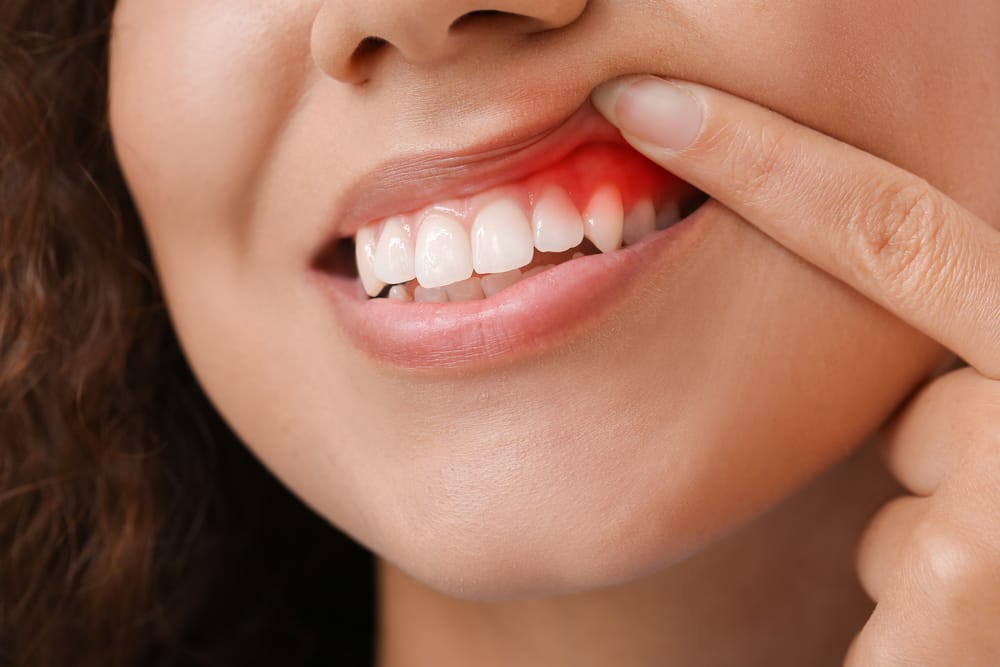
Poor oral hygiene can lead to dental and gum problems, including periodontal disease. Periodontal disease affects the tissues that support teeth; it is caused by bacteria found in dental plaque. If left untreated, it can lead to the loss of teeth and other serious health issues. In this post, we will review everything you need to know about periodontal disease. We will discuss its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. We will also delve into how you can prevent the onset of periodontal disease with good oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups. Read on to learn more about periodontal disease and how to maintain healthy gums.
Common Symptoms Associated with Periodontal Disease
Persistent halitosis, or bad breath, is a common symptom associated with periodontal disease. Additionally, gum inflammation, redness, and tenderness can signal the presence of this oral health condition. Other symptoms include gum recession, tooth sensitivity, and loose teeth. The presence of pus between the gums and teeth is also a significant indicator of periodontal disease. Furthermore, changes in tooth alignment or bite may be associated with gum disease. These symptoms should not be ignored, as early detection and treatment are crucial in preventing further damage.
Role of Oral Hygiene in Periodontal Disease
Daily brushing and flossing play a crucial role in preventing periodontal disease. Regular dental cleanings are essential as they remove plaque buildup and reduce the risk of gum disease. Using mouthwash can supplement oral hygiene practices, helping to control bacterial infection. It’s essential to maintain proper brushing technique, including brushing along the gum line, to ensure periodontal health. Good oral hygiene habits should be instilled from an early age to prevent the development of gum disease.
Other Factors Contributing to Periodontal Disease
Genetic factors can influence an individual’s susceptibility to gum disease, while poor nutrition, particularly a diet high in sugar, can contribute to its development. Stress and hormonal changes, such as puberty, can also impact gum health. Certain medications, like oral contraceptives, can increase the risk of gum disease. Additionally, other health conditions, including heart disease, have been linked to periodontal disease. It is essential to address these factors along with proper oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups to maintain healthy gums.
Standard Diagnostic Procedures for Periodontal Disease
To diagnose periodontal disease, dentists employ various standard diagnostic procedures. These include using periodontal probe measurements to assess the health of the gums and identify any periodontal pockets. X-rays are used to detect bone loss and determine the stage of gum disease. Dentists also evaluate symptoms, dental and medical history, and risk factors. Additionally, dental hygienists perform periodontal charting to monitor changes in gum health over time. The stage of gum disease is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment approach.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatment options are often recommended as the initial step in managing periodontal disease. One such option is scaling and root planing, which involves deep cleaning of the teeth and removal of plaque and tartar above and below the gumline. Antibiotics, both oral and topical, may also be prescribed to control bacterial infection. Laser therapy is another non-surgical option to help remove bacteria and promote tissue regeneration. Additionally, regular professional dental cleanings combined with good oral hygiene practices play a crucial role in treating periodontal disease.
Surgical Treatment Options
Periodontal disease may require surgical intervention in advanced stages when non-surgical treatments are insufficient. Flap surgery involves lifting the gum tissue to access the root surfaces. Bone grafting restores bone loss caused by the disease. Guided tissue regeneration promotes bone and gum tissue regeneration. Soft tissue grafting covers exposed tooth roots, reducing gum recession. Surgical treatment options aim to control the disease, promote healing, and restore oral health. These procedures are typically reserved for severe cases.
Oral Hygiene Practices to Prevent Periodontal Disease
To maintain oral health and prevent periodontal disease, incorporating proper oral hygiene practices is crucial. Brushing teeth twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush helps remove plaque and bacteria. Flossing daily is essential to eliminate plaque buildup between teeth and along the gum line. They are using mouthwash aids in controlling harmful bacteria and maintaining fresh breath. By practicing good oral hygiene, individuals can reduce the risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health problems. Additionally, incorporating proper brushing techniques, such as brushing at a 45-degree angle, effectively cleans teeth and gums.
Regular Dental Check-ups and their Role in Prevention
Regular dental check-ups are crucial in preventing periodontal disease and maintaining oral health. These check-ups allow for the early detection of gum disease symptoms, ensuring timely intervention. Dental professionals can perform professional dental cleanings to remove plaque buildup, essential for preventing gum disease. Additionally, dentists can provide personalized oral hygiene instructions and identify risk factors for gum disease, helping individuals take proactive steps toward prevention. Routine dental exams are vital for monitoring gum health, performing periodontal screenings, and recommending appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing periodontal disease. It is essential to recognize the symptoms associated with periodontal disease and understand the causes and contributing factors. Regular dental check-ups play a significant role in preventing and identifying any gum health issues. With non-surgical and surgical treatment options available, it is possible to manage periodontal disease effectively. However, it is essential to remember that prevention is always better than cure. By adopting proper oral hygiene practices and seeking prompt medical attention when needed, you can protect your gum health and maintain a healthy smile.
 Meet Dr. Leffler
Meet Dr. Leffler
 Meet the Team
Meet the Team
 Dental Membership Plan
Dental Membership Plan
 Insurance Information
Insurance Information
 Patient Forms
Patient Forms
 Online Bill Pay
Online Bill Pay
 Your First Visit
Your First Visit